Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a condition that causes dry, itchy and inflamed skin. It's common in young children but can occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis is long lasting (chronic) and tends to flare sometimes. It can be irritating but it's not contagious.
People with atopic dermatitis are at risk of developing food allergies, hay fever and asthma.
Moisturizing regularly and following other skin care habits can relieve itching and prevent new outbreaks (flares). Treatment may also include medicated ointments or creams
Symptoms
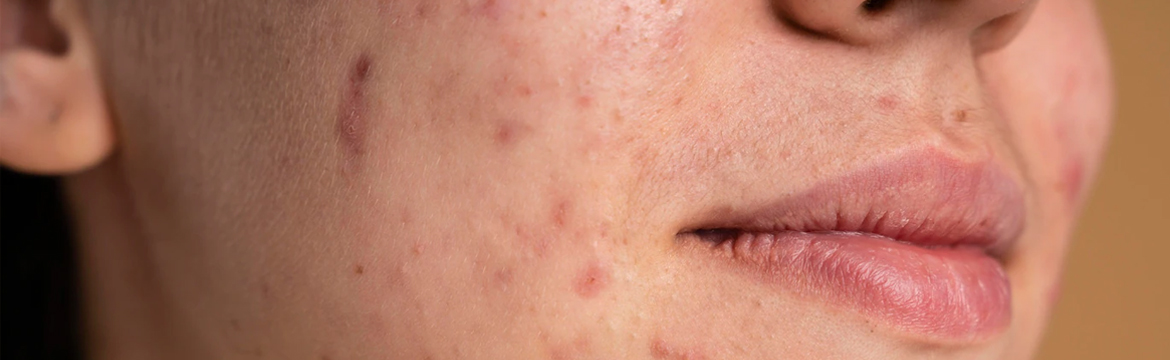
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) symptoms can appear anywhere on the body and vary widely from person to person. They may include:
- Dry, cracked skin
- Itchiness (pruritus)
- Rash on swollen skin that varies in color depending on your skin color
- Small, raised bumps, on brown or Black skin
- Oozing and crusting
- Thickened skin
- Darkening of the skin around the eyes
- Raw, sensitive skin from scratching
Atopic dermatitis often begins before age 5 and may continue into the teen and adult years. For some people, it flares and then clears up for a time, even for several years.
When to see a doctor
Talk with a health care provider if you or your child:
- Has symptoms of atopic dermatitis
- Is so uncomfortable that the condition is affecting sleep and daily activities
- Has a skin infection — look for new streaks, pus, yellow scabs
- Has symptoms even after trying self-care steps
Seek immediate medical attention if you or your child has a fever and the rash looks infected.
Causes
Eczema occurs in people of all ages
In some people, atopic dermatitis is related to a gene variation that affects the skin's ability to provide protection. With a weak barrier function, the skin is less able to retain moisture and protect against bacteria, irritants, allergens and environmental factors — such as tobacco smoke.
In other people, atopic dermatitis is caused by too much of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus on the skin. This displaces helpful bacteria and disrupts the skin's barrier function.
A weak skin barrier function might also trigger an immune system response that causes the inflamed skin and other symptoms.
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is one of several types of dermatitis. Other common types are contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff). Dermatitis isn't contagious.
Risk factors
The main risk factor for atopic dermatitis is having had eczema, allergies, hay fever or asthma in the past. Having family members with these conditions also increases your risk.
Complications
Complications of atopic dermatitis (eczema) may include:
-
Plaque psoriasis
The most common type of psoriasis, plaque psoriasis causes dry, itchy, raised skin patches (plaques) covered with scales. There may be few or many. They usually appear on the elbows, knees, lower back and scalp. The patches vary in color, depending on skin color. The affected skin might heal with temporary changes in color (post inflammatory hyperpigmentation), particularly on brown or Black skin. -
Asthma and hay fever
Many people with atopic dermatitis develop asthma and hay fever. This can happen before or after developing atopic dermatitis. -
Food allergies
People with atopic dermatitis often develop food allergies. One of the main symptoms of this condition is hives (urticaria). -
Chronic itchy, scaly skin
A skin condition called neurodermatitis (lichen simplex chronicus) starts with a patch of itchy skin. You scratch the area, which provides only temporary relief. Scratching actually makes the skin itchier because it activates the nerve fibers in your skin. Over time, you may scratch out of habit. This condition can cause the affected skin to become discolored, thick and leathery. -
Patches of skin that's darker or lighter than the surrounding area
This complication after the rash has healed is called post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation. It's more common in people with brown or Black skin. It might take several months for the discoloration to fade. -
Skin infections
Repeated scratching that breaks the skin can cause open sores and cracks. These increase the risk of infection from bacteria and viruses. These skin infections can spread and become life-threatening. -
Irritant hand dermatitis
This especially affects people whose hands are often wet and exposed to harsh soaps, detergents and disinfectant at work. -
Allergic contact dermatitis
This condition is common in people with atopic dermatitis. Allergic contact dermatitis is an itchy rash caused by touching substances you're allergic to. The color of the rash varies depending on your skin color. -
Sleep problems
The itchiness of atopic dermatitis can interfere with sleep. -
Mental health conditions
Atopic dermatitis is associated with depression and anxiety. This may be related to the constant itching and sleep problems common among people with atopic dermatitis.
Prevention
Developing a basic skin care routine may help prevent eczema flares. The following tips may help reduce the drying effects of bathing:
-
Moisturize your skin at least twice a day
Creams, ointments, shea butter and lotions seal in moisture. Choose a product or products that work well for you. Ideally, the best one for you will be safe, effective, affordable and unscented. Using petroleum jelly on your baby's skin may help prevent development of atopic dermatitis. -
Take a daily bath or shower
Use warm, rather than hot, water and limit your bath or shower to about 10 minutes. -
Use a gentle, nonsoap cleanser
Choose a cleanser that's free of dyes, alcohols and fragrance. For young children, you usually need only warm water to get them clean — no soap or bubble bath needed. Soap can be especially irritating to the skin of young children. For people of any age, deodorant soaps and antibacterial soaps can remove too much of the skin's natural oils and dry the skin. Don't scrub the skin with a washcloth or loofah. -
Pat dry
After bathing, gently pat the skin with a soft towel. Apply moisturizer while your skin is still damp (within three minutes).
The triggers for atopic dermatitis vary widely from person to person. Try to identify and avoid irritants that trigger your eczema. In general, avoid anything that causes an itch because scratching often triggers a flare.
Once you understand what triggers your eczema, talk with your health care provider about how to manage your symptoms and prevent flares.